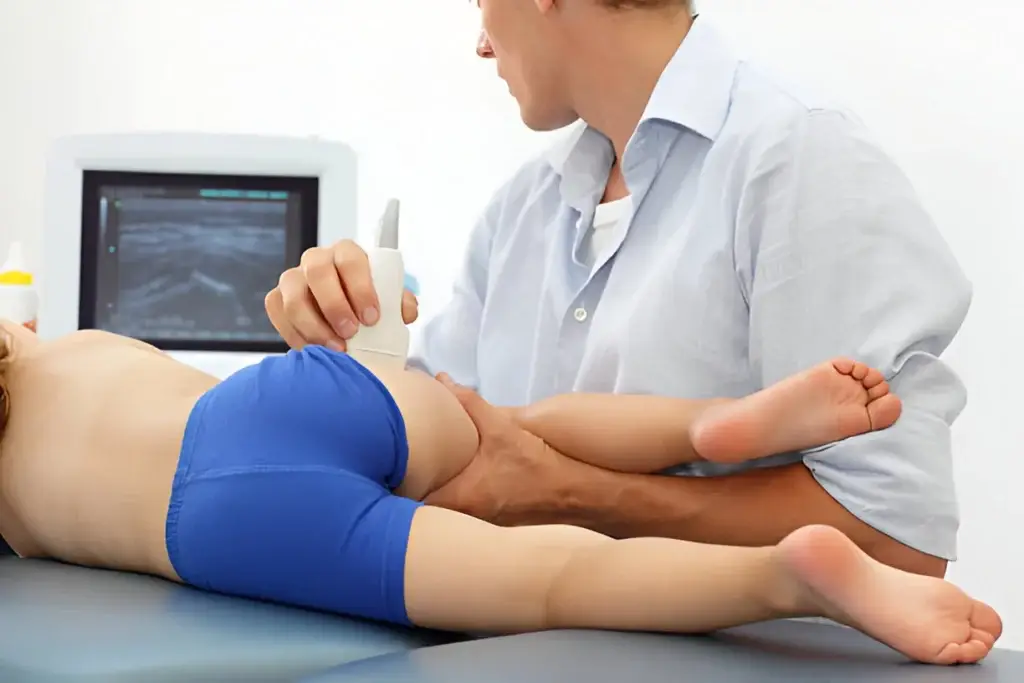
Musculoskeletal (MSK) injections guided by ultrasound are a common and effective technique used to manage pain associated with various musculoskeletal conditions. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
What Are MSK Injections?
MSK injections involve the delivery of medications directly into specific areas of the musculoskeletal system, such as joints, tendons, or bursa. The primary goal is to reduce pain, inflammation, and improve function. Common types of MSK injections include:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Used to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
- Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Often used in joint disorders like osteoarthritis to provide lubrication and improve joint function.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: Utilizes components from the patient’s own blood to promote healing.
- Local Anesthetic Injections: Used for temporary pain relief or as a diagnostic tool.
Stem Cells and Exosomes are examples of injectates that offer a different mechanism of action than some of the previously mentioned solutions. Over the next several months we will discuss what’s new in MSK injections and how they can better help you age gracefully!
Role of Ultrasound in MSK Injections
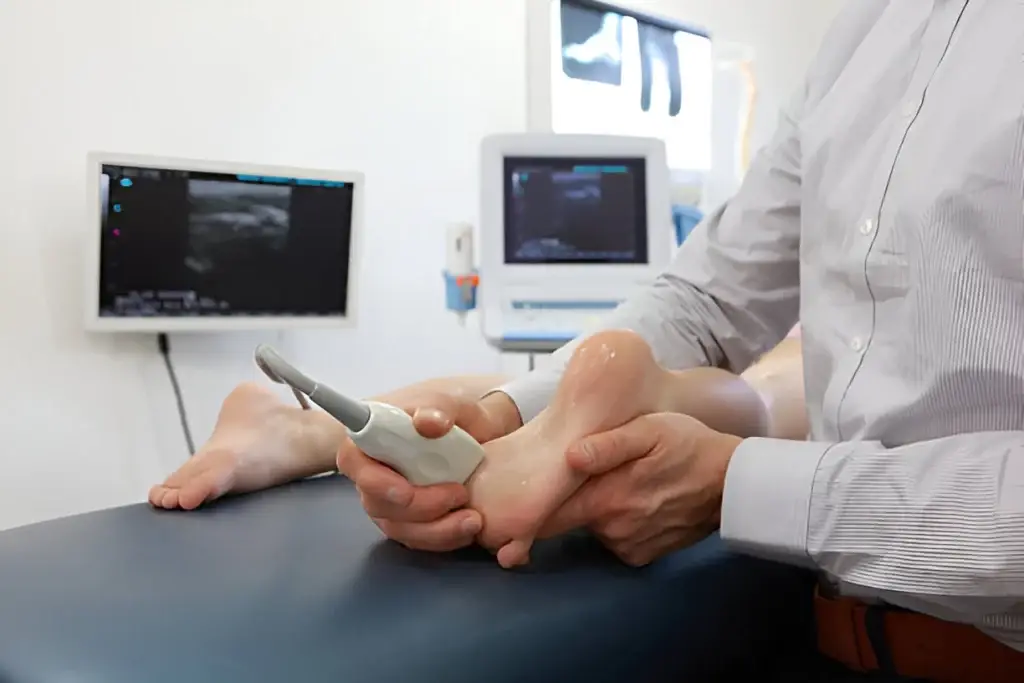
Ultrasound guidance enhances the precision of MSK injections by allowing real-time visualization of anatomical structures. This has several advantages:
- Accuracy: Ultrasound allows for precise needle placement, which increases the effectiveness of the injection and reduces the risk of complications.
- Visualization: It provides clear images of the targeted area, such as the joint space or tendon, helping to avoid nearby structures like nerves or blood vessels.
- Immediate Feedback: The ability to visualize the injection in real time helps confirm the medication’s proper placement.
Procedure for Ultrasound-Guided MSK Injections
- Preparation: The patient is positioned comfortably, and the skin over the injection site is cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
- Ultrasound Imaging: The clinician uses the ultrasound probe to identify the anatomy of the area to be injected. This involves moving the probe to get different views and determine the exact location for the injection.
- Needle Insertion: A thin, sterile needle is inserted through the skin. The clinician monitors the needle’s progress on the ultrasound screen to ensure accurate placement.
- Medication Injection: Once the needle is correctly positioned, the medication is injected into the target area. The clinician may adjust the needle position if necessary, using the ultrasound image as a guide.
Post-Procedure: After the injection, the needle is removed, and a bandage may be applied. The patient is usually observed for a short period to monitor for any immediate reactions.
Benefits

- Reduced Pain and Discomfort: Improved accuracy often results in less pain and discomfort during and after the procedure.
- Enhanced Effectiveness: Targeting the exact area of inflammation or pain can lead to better outcomes.
- Safety: Real-time imaging reduces the risk of injuring surrounding structures.
Considerations and Risks
- Infection: As with any injection, there’s a risk of infection at the injection site.
- Bleeding: Minor bleeding or bruising can occur, especially if the area is vascular.
- Allergic Reactions: Though rare, allergic reactions to injected medications can occur.
- Technique: The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the skill and experience of the clinician performing the injection.
Follow-Up and Care
- Monitoring: Patients may be advised to monitor their symptoms and follow up with their healthcare provider to assess the response to the injection.
- Activity Modification: Temporary activity modification or rest might be recommended to allow the area to heal and to maximize the benefits of the injection.
In Summary, new injectates offer a whole new mechanism to help relieve pain. Multiple studies have been written describing the positive effects of Exosomes and Stem Cells injected in joints.
FAQs
Q: How long does it take to see results from PRP injections?
A: Most patients start to see improvement within a few weeks, with full benefits typically seen after a few months.
Q: Are PRP injections painful?
A: The injection itself may cause some discomfort, but most patients tolerate the procedure well. Any post-injection pain is usually mild and temporary.
Q: How many PRP injections will I need?
A: The number of injections needed varies depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient. Your healthcare provider will develop a treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Q: Are there any side effects of PRP injections?
A: Because PRP injections use your own blood, side effects are minimal. Some patients may experience mild pain or swelling at the injection site, but serious side effects are rare.
Q: Can PRP injections be combined with other treatments?
A: Yes, PRP injections can be used alongside other treatments, such as physical therapy or other types of injections, to enhance overall results.